Design of Micro-Surgical Manipulators for Dual-arm Microsurgery
Active Personnel:
The purpose of this project is to develop a comprehensive robotic system for micro surgeries, e.g. ophthalmic surgery, and to assist surgeons with higher precision, less tremor, and more ease to manipulate the eyeball.
- Wei Wei 2006-2009
- Roger Goldman 2007
- Haoran Yu 2010
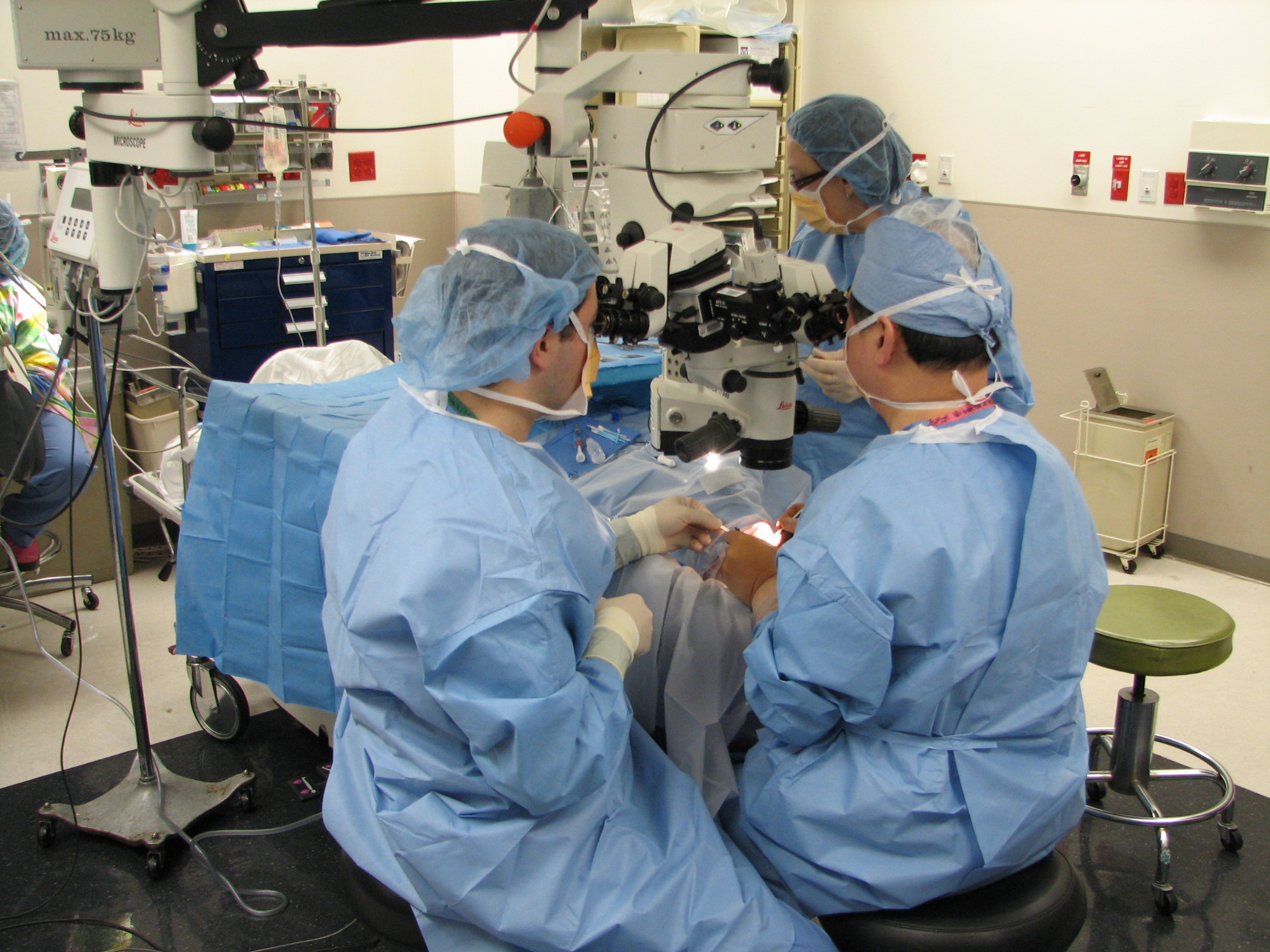
An Overview of the Ophthalmic Surgery Setup
In an ophthalmic surgery setup, two surgeons coordinate activities to perform the ophthalmic surgical procedures. The main surgeon sits superior to the patient'ss head and performs most of the surgical tasks including manipulation of the surgical tools and the light source. The assistant surgeon sits beside the patient's head to provide irrigation and removal of fluids and to adjust the placement of the visualization of the external lenses. There is also another assistant sitting on the other side of the patient for tool delivery to the main surgeon.
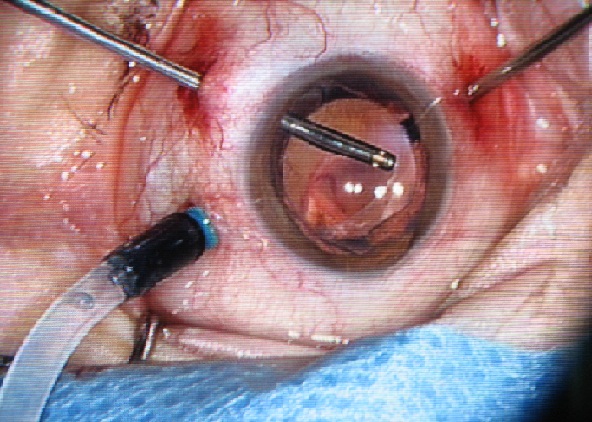
Three incisions are typically made in the sclera to provide access to the inner vitreous body for one irrigation tube, one light source and one surgical instrument. The irrigation tube injects liquid to maintain intraocular pressure. The light source illuminates an area on the retina for proper visualization under the microscope. The surgical tools including picks, micro tweezers, vitrectomy cutters and other laser ablation devices vary dependent on the requirements of the procedure. The surgeons operate using a microscope while visualizing the retina through a dilated iris. Because the visual field does not include the entire retinal surface, the surgery often requires to tilt the eye under the microscope in order to view peripheral areas of the retina.
 |
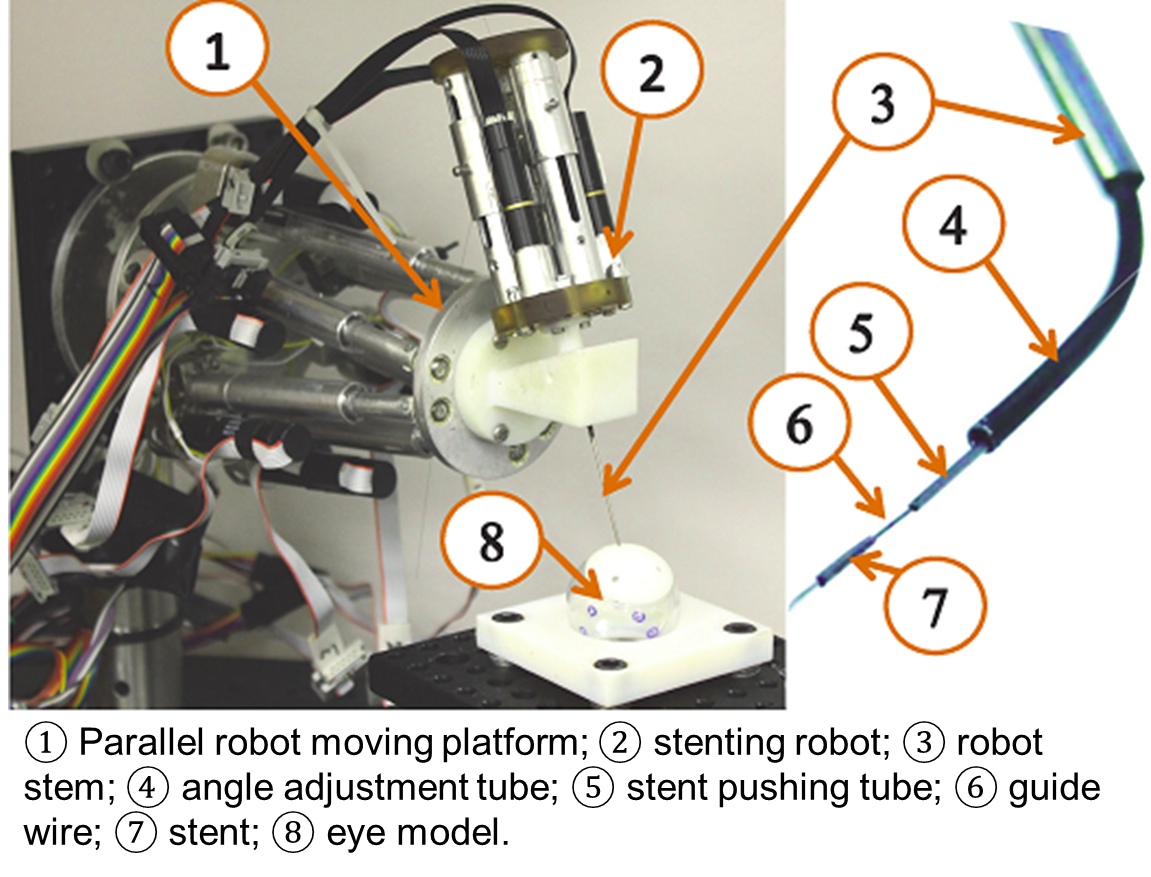 |
| Robot Setup for an Ophthalmic Surgery | The 3-DoF Intro_Ocular Dexterity Robot (Stenting Robot) |
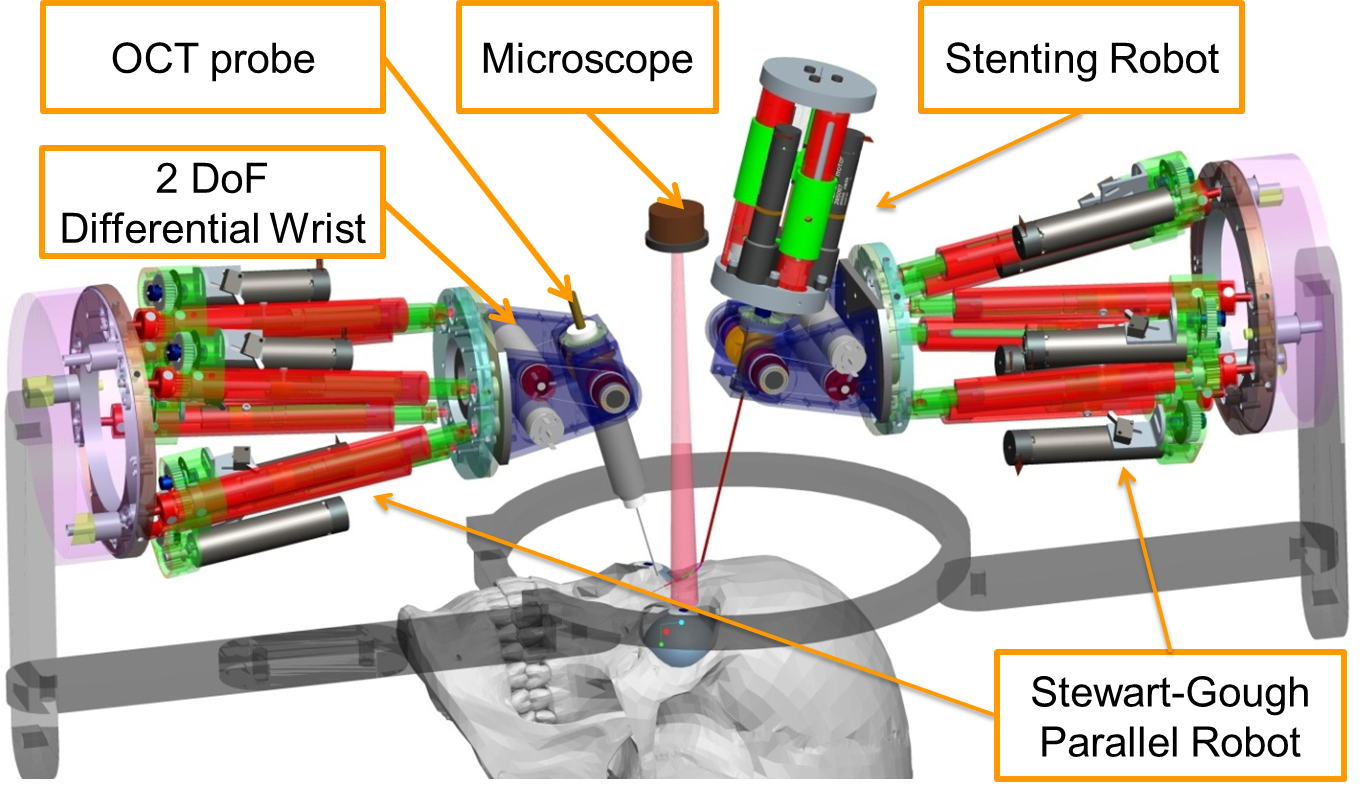
Our role in this project is to design a 16-DoF hybrid robotic system to assist ophthalmic surgery as shown in the above figure. This system will allow high precision dexterous manipulation of surgical instruments within the vitreous body of the eye and macroscopic rotation of the eye for surgical field visibility. A frame is secured without trauma to the patient's head with a locking bite-plate and coronal strap that rigidly affixes the frame to the patient. Two identical hybrid robotic arms are rigidly attached to this frame. Each robotic arm is composed from a 2 DoF IODR (Intra-Ocular Dexterity Robot) and a 6 DoF parallel robot. This design will allow 5 DoFs for the surgical tools inside the eye, as compared to 4 DoF tools used currently. The 2 DoF IODR provides intra-ocular dexterity while the parallel robot provides global precise positioning of the eye and the surgical tool inside the eye. The IODR utilizes a pre-shaped NiTi tube that bends in one DoF as it is extended outside of a straight cannula. The cannula of the IODR rotates about its axis to provide the second DoF inside the eye. For the parallel robot, we propose the Stewart-Gough platform design due to its rigidity, compactness, positional accuracy, and high payload-to-weight ratio.
An initial performance evaluation is implemented to compare the dexterity between the robotic arms without distal dexterity and with distal dexterity. We plot the KCI (Kinematic Conditioning Index) measurement for both translational and rotational motions.
.style2 { font-family: Arial,Helvetica,sans-serif; }
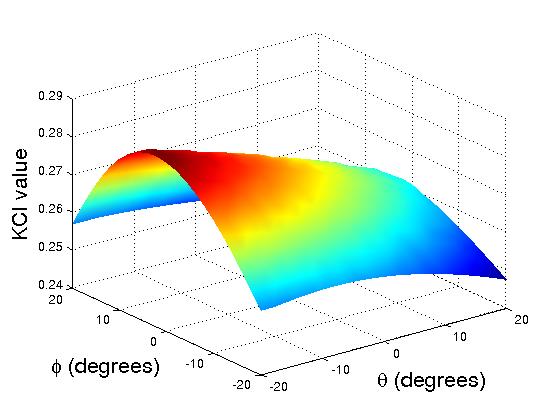 |
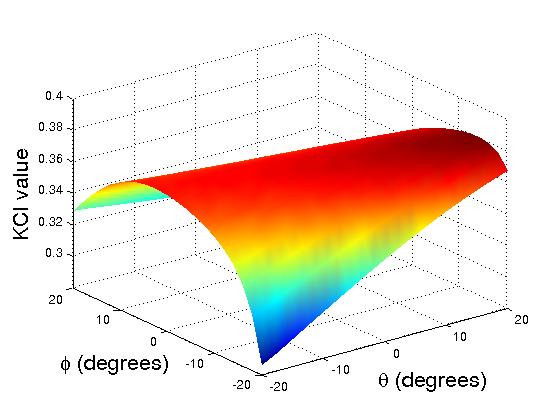 |
Translational KCI Plots for One Arm without Distal Dexterity (left) and with Distal Dexterity (right)
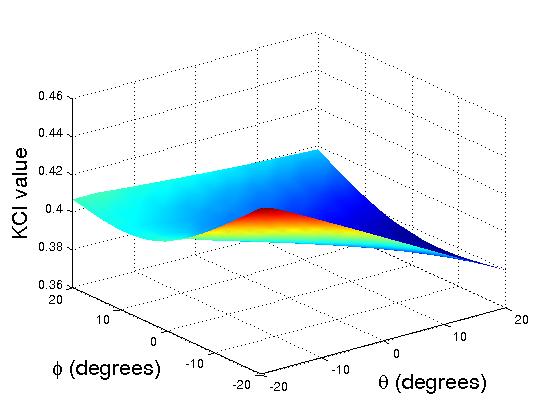 |
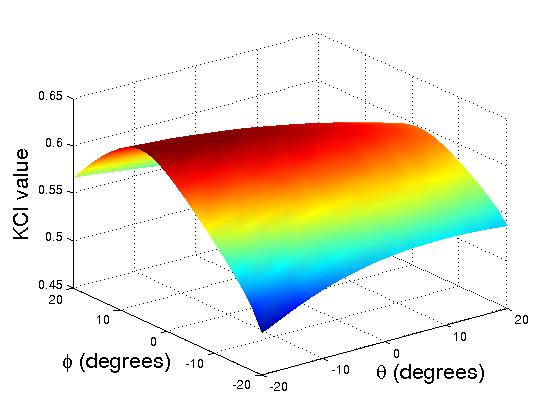 |
Rotational KCI Plots for One Arm without Distal Dexterity (left) and with Distal Dexterity (right)
Publications
- Yu, H., Shen, J. H., Shah, R. J., Simaan, N., and Joos, K. M. (2015), "Evaluation of microsurgical tasks with OCT-guided and/or robot-assisted ophthalmic forceps", Biomedical Optics Express, Vol. 6, No. 2, pp. 457--472, 2015.
- Yu, H., Shah, R. J., Shen, J. H., Joos, K. M. and Simaan, N. (2014). "Preliminary Evaluation of a Robotic Retinal Surgical Manipulator", In 2014 The Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology Annual Conference (ARVO'2014).
- Yu, H., Shen, J. H., Joos, K. M. and Simaan, N. (2013). "Design , Calibration and Preliminary Testing of A Robotic Telemanipulator for OCT guided Retinal Surgery". IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp.225-231, 2013.
- Shen, J. H., Yu, H., Simaan, N. and Joos, K. M. (2013). "A Robotic-controlled Intraocular OCT Probe", Investigative Ophtalmology and Visual Science, Vol 54, No. 6, pp. 1502, 2013.
- Wei, W. and Simaan, N., "Modeling, Force Sensing and Control of Flexible Cannulas for Micro-Stent Delivery," ASME Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement, and Control, Vol 134, No. 4, pp. 041004, 2012.
- Fine, H. and Wei, W. and Simaan, N., "Could Robots Ever Do Retina Surgery?" Review of Ophthalmology, Vol 17, No. 5, 2010.
- Wei, W. and Popplewell, C. and Fine, H. and Chang, S. and Simaan, N., "Enabling Technology for Micro-Vascular Stenting in Ophthalmic Surgery," ASME Journal of Medical Devices (JMED), Vol 4, No. 2, pp. 01450301--06, 2010.
- Fine, H. and Wei, W. and Chang, S. and Simaan, N., "A novel dual-arm dexterous ophthalmic microsurgical robot: applications for retinal vascular cannulation and stent deployment," ASME Journal of Mechanisms and Robotics (JMR), Vol 2, No. 1, pp. 11010-11012, 2010.
- Wei, W., Goldman, R., Fine, H., Chang, S., Simaan, N., “Modeling and Performance Evaluation of Hybrid Multi-Arm Robots Operating on Hollow Suspended Organs,” IEEE Transactions on Robotics, Vol 25, No. 1, pp. 147-157, 2009.
- Wei, W., Goldman, R., Simaan, N., Fine, H., Chang, S., "Design and Theoretical Evaluation of Micro-Surgical Manipulators for Orbital Manipulation and Intraocular Dexterity," International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 3389-3395, 2007.
Collaborators:
Dr. Stanley Chang & Dr. Howard Fine
Department of Ophthalmology, Columbia University.
Dr. Karen M. Joos & Dr. Jin-Hui Shen
Vanderbilt Eye Institute, Vanderbilt University.
Acknowledegment:
This project is currently funded by the Vanderbilt Discovery Grant 4229990095. The project name is
''OCT-Assisted Robotic Micro-Vascular Retinal Surgery''

