- This investigation focused on parallel robots that adapt their geometry according to task requirements, i.e., variable geometry parallel robots. These robots have a set of variable geometry parameters that can be controlled to modify their characteristics to accommodate a given task requirement. The main objective for changing the geometry of these robots was the stiffness. Two methods to achieve stiffness modification were studied by using either actuation or kinematic redundancy to result in a virtual or real geometry change in the kinematic chains, , Figure 1.
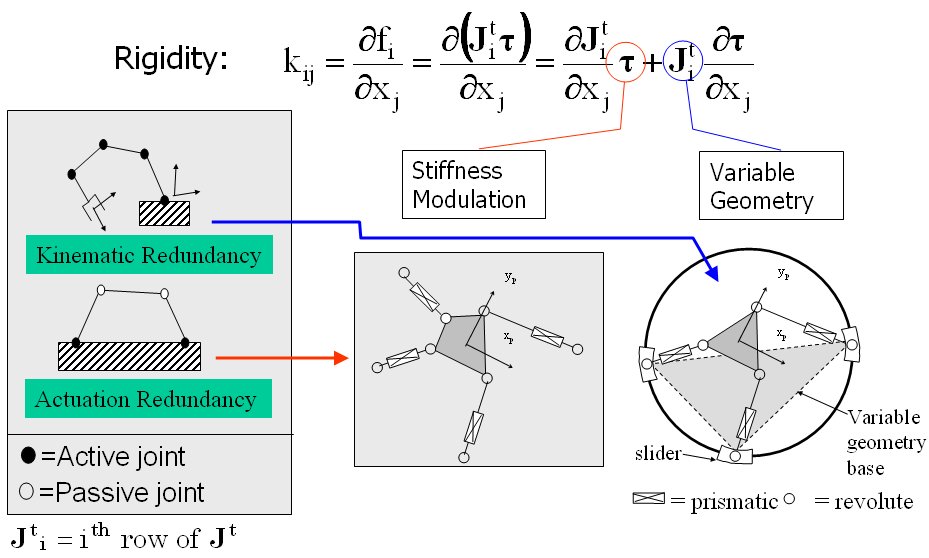
Figure 1: the focus of this research is on the use of actuation and kinematic redundancy for stiffness modulation and stiffness synthesis
- In this work I studied two aspects of stiffness modulation and stiffness synthesis while using line geometry tools and algebraic geometry tools to explain second order singularities of the stiffness modulation problem and to solve the stiffness synthesis problem for parallel robots with kinematic redundancy (variable geometry parallel robots). The problem of stiffness modulation for parallel robots using actuation redundancy was treated before by numerous researcher, but the problem of the singularities associated with the stiffness moduloation was never given a geometric physical interpretation. In ASME JMD paper it was proved that the Jacobian derivatives are composed of 36 lines in space. A geometric representation for all the stiffness control singularities including “second–order singularities” was obtained using line geometry. This method provided guidelines for preventing architecture singularities from stiffness control point of view - even for parallel robots with actuation redundancy. This provided a simple method for the design planar parlellel robots with actuation redunadancy.This work is also relevant to fixturing, graspin using multi-fingered hands, and the stability of wire-actuated robots.
- Subsequently, I focused on the problem of stiffness synthesis for parallel robots with kinematic redundancy. The main problem I addressed was to find a solution methodology for the problem of stiffness synthesis of these robots given a limited set of free geometric parameters. The solution methodology I used addresses questions of solvability and the space of achievable stiffness using a given set of free redundant variable-geometry parameters. The method relies on the use of algebraic geometry methods including Groebner bases, multiplication table over residue classes, and eigenvalues of multiplication tables for obtaininig solutions of the stiffness syntheis problem (a synopsis of this method is shown in Figure 2 and 3). In IJRR 2003 journal paper a 6 DoF variable geometry robot with 12 actuators shown in Figure 4. The problem of stiffness synthesis of this robot was analyzed while answering questions on solvability and the space of achievable stiffness using a given set of free redundant variable-geometry parameters. I used algebraic geometry methods and Groebner bases to solve this problem. It has been shown that up to 48*48 solutions exist for this problem and an example of a synthesis problem demonstrating 384 real solutions was presented. Figure 5 demonstrates the use of Groebner bases to obtain solvability maps for the stiffness synthesis given a limited set of free geometric parameters. Figure 6 shows all the 384 real solutions found for the problem of stiffness synthesis of the variable geometry parallel robot of Figure 4.
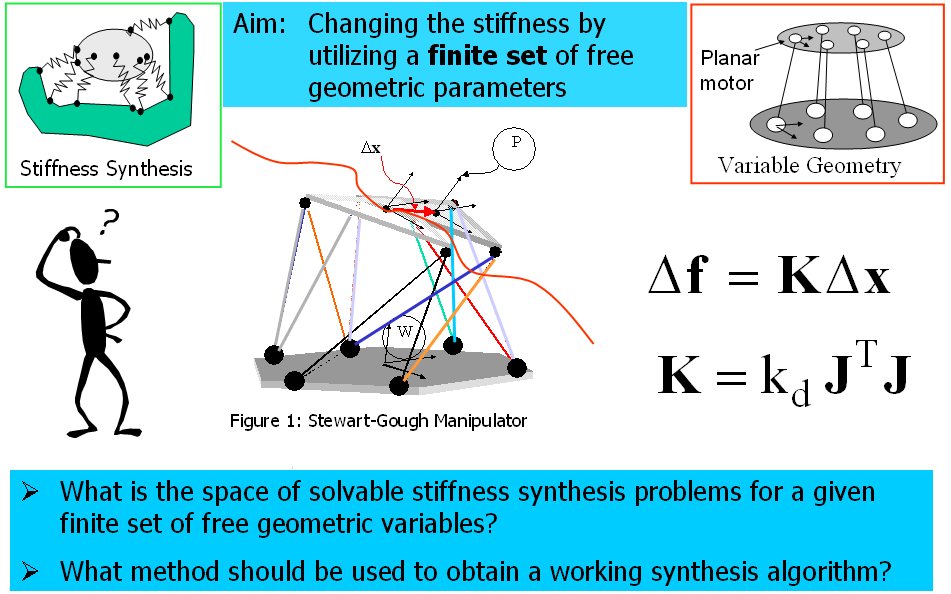
Figure 2: the problem of stiffness synthesis using a limited set of free geometric parameter that can be used to achieve desirable stiffness of parallel robots with kinematic redundancy
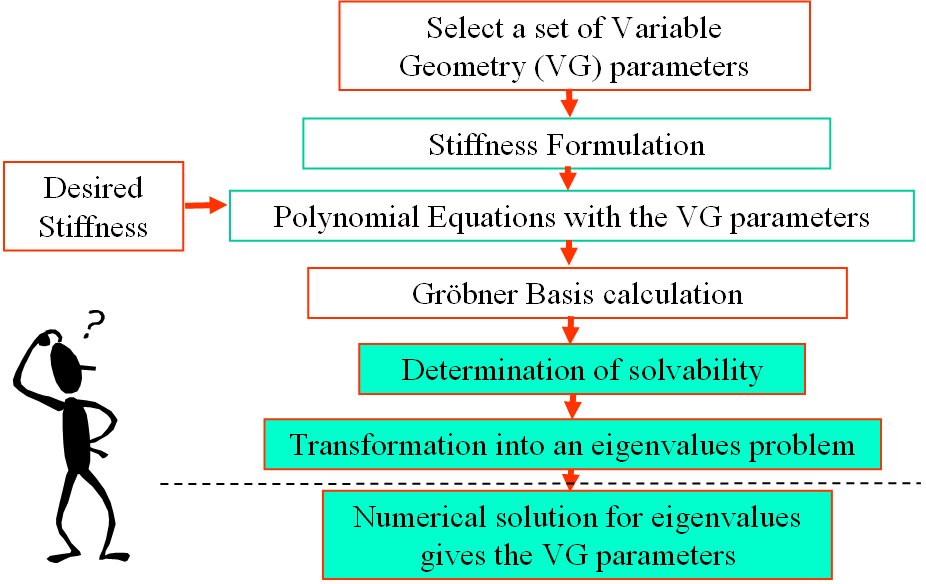
Figure 3: the solution method used for the problem of stiffness syhthesis of parallel robots with kinematic redundancy
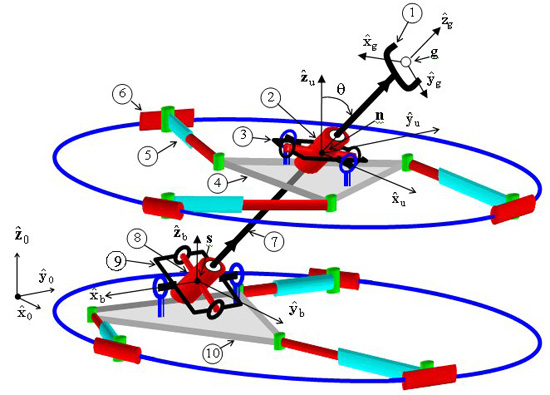
Figure 4: an example of a six DoF parallel robots with 12 actuators (parallel robot with kienmatic redundancy)
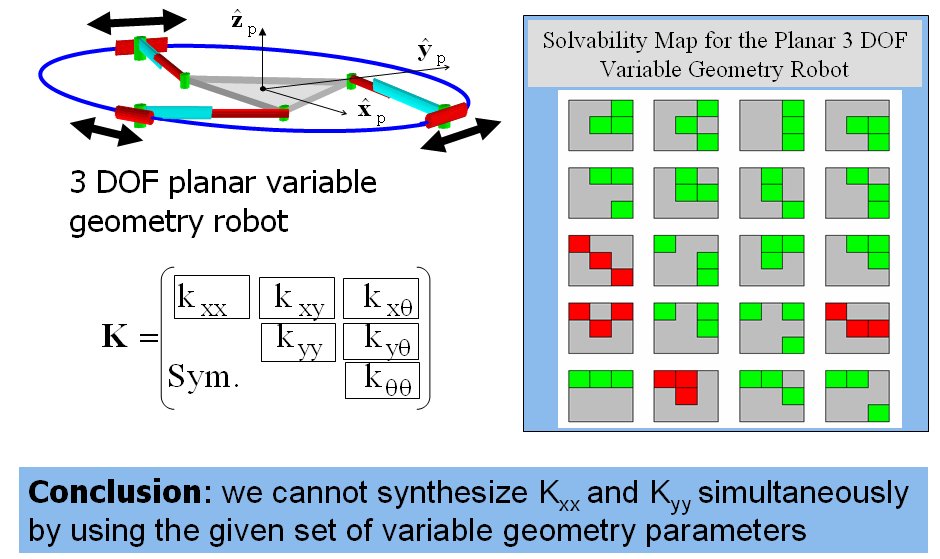
Figure 5: the solvability map for the stiffness synthesis problem of a planar parallel robot with six actuators. The green blocks designate stiffness components that can be synthesized independently using the given set of variable geometry parameters. In this example the variable geometry parameters are the locations of the three sliders on the circular base.
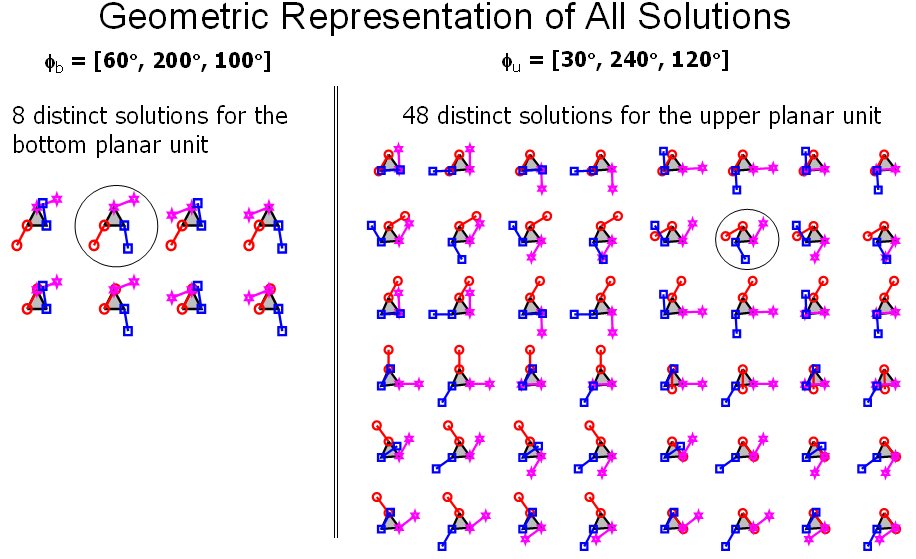
Figure 6: 384 possible real solutions for the problem of stiffness synthesis of the paralllel robot in figure 3. This problem was proven to have at most 48^2 solutions in the complex domain.